Page 11 - IMCJ19s1
P. 11
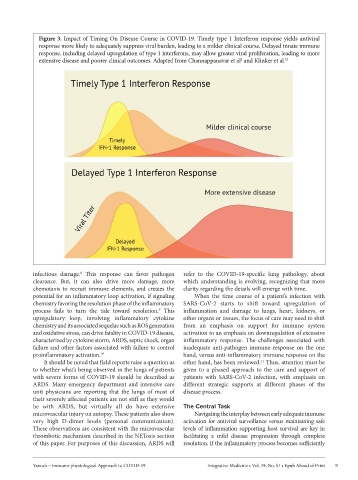
Figure 3. Impact of Timing On Disease Course in COVID-19. Timely type 1 Interferon response yields antiviral
response more likely to adequately suppress viral burden, leading to a milder clinical course. Delayed innate immune
response, including delayed upregulation of type 1 interferons, may allow greater viral proliferation, leading to more
extensive disease and poorer clinical outcomes. Adapted from Channappanavar et al and Klinker et al.
5
11
infectious damage. This response can favor pathogen refer to the COVID-19-specific lung pathology, about
8
clearance. But, it can also drive more damage, more which understanding is evolving, recognizing that more
chemotaxis to recruit immune elements, and creates the clarity regarding the details will emerge with time.
potential for an inflammatory loop activation, if signaling When the time course of a patient’s infection with
chemistry favoring the resolution phase of the inflammatory SARS-CoV-2 starts to shift toward upregulation of
process fails to turn the tide toward resolution. This inflammation and damage to lungs, heart, kidneys, or
9
upregulatory loop, involving inflammatory cytokine other organs or tissues, the focus of care may need to shift
chemistry and its associated sequelae such as ROS generation from an emphasis on support for immune system
and oxidative stress, can drive fatality in COVID-19 disease, activation to an emphasis on downregulation of excessive
characterized by cytokine storm, ARDS, septic shock, organ inflammatory response. The challenges associated with
failure and other factors associated with failure to control inadequate anti-pathogen immune response on the one
proinflammatory activation. 10 hand, versus anti-inflammatory immune response on the
It should be noted that field reports raise a question as other hand, has been reviewed. Thus, attention must be
11
to whether what’s being observed in the lungs of patients given to a phased approach to the care and support of
with severe forms of COVID-19 should be described as patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, with emphasis on
ARDS. Many emergency department and intensive care different strategic supports at different phases of the
unit physicians are reporting that the lungs of most of disease process.
their severely affected patients are not stiff as they would
be with ARDS, but virtually all do have extensive The Central Task
microvascular injury on autopsy. These patients also show Navigating the interplay between early adequate immune
very high D-dimer levels (personal communication). activation for antiviral surveillance versus maintaining safe
These observations are consistent with the microvascular levels of inflammation supporting host survival are key in
thrombotic mechanism described in the NETosis section facilitating a mild disease progression through complete
of this paper. For purposes of this discussion, ARDS will resolution. If the inflammatory process becomes sufficiently
Yanuck—Immuno-physiological Approach to COVID-19 Integrative Medicine • Vol. 19, No. S1 • Epub Ahead of Print 9