Page 41 - IMCJ19s1
P. 41
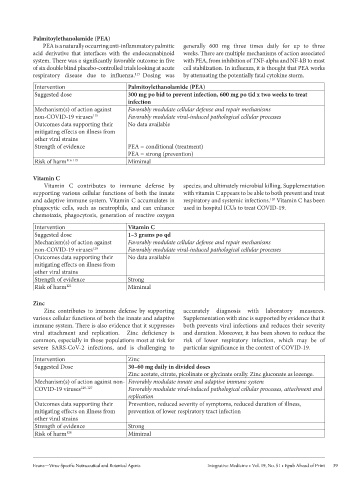
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA)
PEA is a naturally occurring anti-inflammatory palmitic generally 600 mg three times daily for up to three
acid derivative that interfaces with the endocannabinoid weeks. There are multiple mechanisms of action associated
system. There was a significantly favorable outcome in five with PEA, from inhibition of TNF-alpha and NF-kB to mast
of six double blind placebo-controlled trials looking at acute cell stabilization. In influenza, it is thought that PEA works
respiratory disease due to influenza. 115 Dosing was by attenuating the potentially fatal cytokine storm.
Intervention Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA)
Suggested dose 300 mg po bid to prevent infection, 600 mg po tid x two weeks to treat
infection
Mechanism(s) of action against Favorably modulate cellular defense and repair mechanisms
non-COVID-19 viruses 115 Favorably modulate viral-induced pathological cellular processes
Outcomes data supporting their No data available
mitigating effects on illness from
other viral strains
Strength of evidence PEA = conditional (treatment)
PEA = strong (prevention)
Risk of harm 116-119 Mimimal
Vitamin C
Vitamin C contributes to immune defense by species, and ultimately microbial killing. Supplementation
supporting various cellular functions of both the innate with vitamin C appears to be able to both prevent and treat
and adaptive immune system. Vitamin C accumulates in respiratory and systemic infections. Vitamin C has been
120
phagocytic cells, such as neutrophils, and can enhance used in hospital ICUs to treat COVID-19.
chemotaxis, phagocytosis, generation of reactive oxygen
Intervention Vitamin C
Suggested dose 1–3 grams po qd
Mechanism(s) of action against Favorably modulate cellular defense and repair mechanisms
non-COVID-19 viruses 120 Favorably modulate viral-induced pathological cellular processes
Outcomes data supporting their No data available
mitigating effects on illness from
other viral strains
Strength of evidence Strong
Risk of harm 121 Mimimal
Zinc
Zinc contributes to immune defense by supporting accurately diagnosis with laboratory measures.
various cellular functions of both the innate and adaptive Supplementation with zinc is supported by evidence that it
immune system. There is also evidence that it suppresses both prevents viral infections and reduces their severity
viral attachment and replication. Zinc deficiency is and duration. Moreover, it has been shown to reduce the
common, especially in those populations most at risk for risk of lower respiratory infection, which may be of
severe SARS-CoV-2 infections, and is challenging to particular significance in the context of COVID-19.
Intervention Zinc
Suggested Dose 30–60 mg daily in divided doses
Zinc acetate, citrate, picolinate or glycinate orally. Zinc gluconate as lozenge.
Mechanism(s) of action against non- Favorably modulate innate and adaptive immune system
COVID-19 viruses 120-127 Favorably modulate viral-induced pathological cellular processes, attachment and
replication
Outcomes data supporting their Prevention, reduced severity of symptoms, reduced duration of illness,
mitigating effects on illness from prevention of lower respiratory tract infection
other viral strains
Strength of evidence Strong
Risk of harm 128 Mimimal
Evans—Virus-Specific Nutraceutical and Botanical Agents Integrative Medicine • Vol. 19, No. S1 • Epub Ahead of Print 39