Page 51 - IMCJ19s1
P. 51
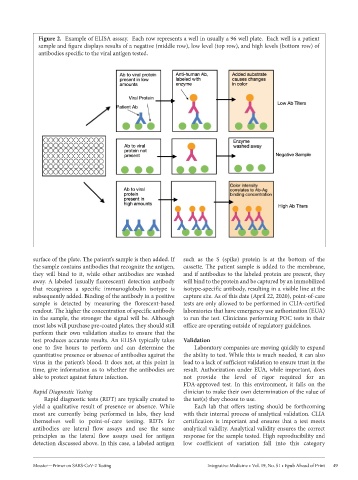
Figure 2. Example of ELISA asssay. Each row represents a well in usually a 96 well plate. Each well is a patient
sample and figure displays results of a negative (middle row), low level (top row), and high levels (bottom row) of
antibodies specific to the viral antigen tested.
surface of the plate. The patient’s sample is then added. If such as the S (spike) protein is at the bottom of the
the sample contains antibodies that recognize the antigen, cassette. The patient sample is added to the membrane,
they will bind to it, while other antibodies are washed and if antibodies to the labeled protein are present, they
away. A labeled (usually fluorescent) detection antibody will bind to the protein and be captured by an immobilized
that recognizes a specific immunoglobulin isotype is isotype-specific antibody, resulting in a visible line at the
subsequently added. Binding of the antibody in a positive capture site. As of this date (April 22, 2020), point-of-care
sample is detected by measuring the florescent-based tests are only allowed to be performed in CLIA-certified
readout. The higher the concentration of specific antibody laboratories that have emergency use authorization (EUA)
in the sample, the stronger the signal will be. Although to run the test. Clinicians performing POC tests in their
most labs will purchase pre-coated plates, they should still office are operating outside of regulatory guidelines.
perform their own validation studies to ensure that the
test produces accurate results. An ELISA typically takes Validation
one to five hours to perform and can determine the Laboratory companies are moving quickly to expand
quantitative presence or absence of antibodies against the the ability to test. While this is much needed, it can also
virus in the patient’s blood. It does not, at this point in lead to a lack of sufficient validation to ensure trust in the
time, give information as to whether the antibodies are result. Authorization under EUA, while important, does
able to protect against future infection. not provide the level of rigor required for an
FDA-approved test. In this environment, it falls on the
Rapid Diagnostic Testing clinician to make their own determination of the value of
Rapid diagnostic tests (RDT) are typically created to the test(s) they choose to use.
yield a qualitative result of presence or absence. While Each lab that offers testing should be forthcoming
most are currently being performed in labs, they lend with their internal process of analytical validation. CLIA
themselves well to point-of-care testing. RDTs for certification is important and ensures that a test meets
antibodies are lateral flow assays and use the same analytical validity. Analytical validity ensures the correct
principles as the lateral flow assays used for antigen response for the sample tested. High reproducibility and
detection discussed above. In this case, a labeled antigen low coefficient of variation fall into this category
Messier—Primer on SARS-CoV-2 Testing Integrative Medicine • Vol. 19, No. S1 • Epub Ahead of Print 49